With the 2022 year quickly coming to an end, we take this opportunity to remind our clients and readers of the annual compliance obligations for enterprises in Cambodia. With each year that passes there seem to be more compliance obligations, and the latest 2023 compliance requirements continue this trend.
With that in mind, we have provided below what we believe are the most important annual compliance requirements that enterprises in Cambodia should be aware of. Compliance requirements may vary depending on a number of factors. In all cases, we encourage you to seek expert advice from a professional advisor about the compliance requirements that may be applicable to your enterprise.
2022 Tax on Income Return
The standard 2022 tax year in Cambodia runs from 1 January to 31 December 2022. Electronic-filing for the 2022 annual Tax on Income (TOI) declaration and associated payment receipt of Tax on Income or Minimum Tax with the General Department of Taxation (GDT) must be completed by 31 of March 2023 or within three (3) months after the end of the tax year for enterprises that have a non-standard tax year.
Those self-assessment taxpayers (taxpayers who are registered with the GDT) that have local branches are required to file a consolidated 2022 TOI declaration attaching the financials of the respective local branches with the return. Self-assessment taxpayers that have both Qualified Investment Project (QIP) and non-QIP activities are required to submit their annual 2022 TOI return in accordance with Prakas 1127 MEF.P dated 11 October, 2016.
All self-assessment taxpayers filing annual 2022 TOI returns with the GDT are required to include a balance sheet, profit-and-loss account and an annexed list of any related party transactions carried out during the 2022 tax year.
2022 Local Transfer Pricing File
The prevailing Cambodia transfer pricing regulation, Prakas No. 986. MEF.P. dated 10 October 2017, requires self-assessment taxpayers that have related party transactions (RPTs) during the 2022 tax year to comply with two annual requirements:
- Completion of a transfer pricing declaration which is annexed to the 2022 annual TOI return and submitted to the GDT;
- Completion of a 2022 local transfer pricing file, the completion of which is acknowledged in the 2022 TOI return.
Some important points that self-assessment taxpayers should pay attention to:
- A local transfer pricing file that has been prepared for an earlier tax year does not in itself meet the requirement for the 2022 tax year. In other words – a stand-alone local transfer pricing file needs to be prepared for each tax year for those Cambodian entities that have ongoing or new RPTs in 2022.
- Self-assessment taxpayers should also be aware that transfer pricing benchmarks used in a local transfer pricing file should be tested annually and updated when appropriate. It is also recommended that the benchmarking analysis be refreshed in full every three (3) years.
- Penalties may apply for non-compliance with the requirements set out above. Perhaps more importantly not having local transfer pricing documentation in place to support a taxpayers RPT’s allows the GDT to more easily argue that payments that are made or received do not follow the arms length principle and to then re-assess taxes, penalties and interest accordingly.
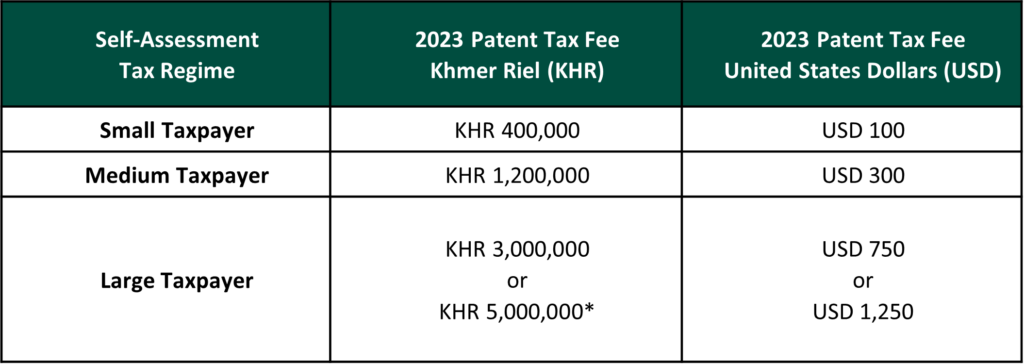
2023 Patent Tax
All self-assessment taxpayers operating in Cambodia are required to register and pay their 2023 Patent Tax with the GDT by 31 of March 2023 for each business activity that they carry out. The amount of Patent Tax payable in 2023 is dependent on the particular classification of the enterprise under the self-assessment regime of taxation. The 2023 Patent Tax fees are as follows:
*If the annual turnover of the Large Taxpayer exceeds KHR 10 billion (USD 2.5 million) then the Patent Tax payable will be USD 1,250. If the annual turnover of the Large Taxpayer is less than KHR 10 billion (USD 2.5 million) the Patent Tax payable will be USD 750.
Application for Annual Certificate of Compliance
All Cambodia enterprises that are recognized as a QIP are required to submit an annual application for a Certificate of Compliance (“COC”) to the Council for the Development of Cambodia by 31 of March of each year following the year in which they obtained their Final Registration Certificate. If a QIP entity fails to obtain a COC it may lose its investment incentives.
Submission of Annual Financial Statements
Enterprises with Audited Financial Statements
Entities that are required to obtain external audited financial statements under Prakas 563 are required to submit their audited financial statements with the Accounting and Auditing Regulator (ACAR), using the ACAR e-filing system, no later than 6 months and 15 days after the close of their accounting period, which for most entities will be 15 July 2023.
Enterprises without Unaudited Financial Statements
Under Instruction No. 002 AAR.N entities that are not required to have their 2022 financial statements externally audited under Prakas 563, are now required to submit their 2022 unaudited financial statements through ACAR’s e-filing system no later than 3 months and 15 days after the close of the accounting period which for most entities will be by 15 April 2023.
To complete the submission process, entities are required to first register with the ACAR online system and then secondly complete the templates provided by ACAR regarding the presentation of their financial statements. Once completed these documents must be uploaded and submitted to ACAR.
Notification regarding use of English
Notification 057 AAR, dated 21 July 2022, requires enterprises that have been registered before 21 July 2022 to submit a application to ACAR for the use of English language in their accounting system before 31 of December 2022.
For enterprises established after 21 July 2022 they are required to submit a application within 180 days from the date of their registration with the GDT.
Failure to comply with the above obligations regarding the ACAR will result in penalties being imposed.
Corporate Secretarial Services
The Amendments to the Law on Commercial Enterprises dated 29 January 2022 provided that all limited liability companies incorporated in Cambodia are required to appoint a corporate secretary who permanently resides in Cambodia.
DFDL offers annual corporate secretarial services that typically include the maintenance of statutory records, ensuring compliance with ongoing corporate governance requirements such as share certificates, share register, quarterly board meetings and annual general meetings.
Annual Declaration of Commercial Enterprise
Following the issuance by the Ministry of Commerce (“MOC”) of the Prakas on the filing of Annual Declaration of Commercial Enterprises (“ADCE”), dated 5 April 2017, an ADCE must now be submitted by each enterprise to the MOC using its online system.
Use of the online system for submission of an ADCE is now compulsory and must be performed within three months from the anniversary of the enterprise’s re-registration on the MOC’s online system. A submission made after the three month period will be subject to a penalty of KHR 2,000,000 (approx. USD 500) imposed by the MOC.
National Domain Names
On 1 April 2022, the MOC and the Ministry of Posts and Telecommunications issued a Joint Notification (Notification 0837) which set out requirements for locally registered companies to use a level 2 national domain name “.com.kh” and e-mail address with a level 2 national domain name “.com.kh.”
If a locally registered company does not have an e-mail address with a level 2 national domain name it must apply for such domain name from the Telecommunication Regulator of Cambodia as soon as possible in order to comply with the requirements set out under Sub-Decree 287 dated 31 December 2021.
Under Article 5 of Sub-Decree 287, a level 2 national domain name includes:
- a domain name ending with “.com.kh” designated for a business enterprise or public enterprise;
- a domain name ending with “.org.kh” designated for an organization, association and union;
- a domain name ending with “.edu.kh” designated for a public and private educational institution;
- a domain name ending with “.net.kh” designated for a company or institution providing computer network services; and
- a domain name ending with “.gov.kh” designated for ministries and state institutions.
Except for a domain name ending with “.gov.kh,” all other domain names have a validity of one year from the date of registration and are renewable by paying an annual fee. After expiration, if the renewal fee is not paid, the domain name will be suspended temporarily. After sixty (60) days without payment, the domain name will be deleted from the system. The domain name may also be deleted if requested by the domain owner or pursuant relevant laws and regulations.
In addition, from 1 January 2023 onwards, when filing an ADCE, all companies must provide the MOC with an email address having a level 2 national domain name. Joint Notification 0837 does not specify whether non-compliance with the above requirements will subject a company to any monetary fines.
Labour Compliance
Foreign Employee Quota for 2023
Enterprises employing or intending to employ foreign employees are required to apply for a foreign employee quota via the Ministry of Labour and Vocational Training (“MLVT”) online system.
All applications must be submitted by the required deadline each year. Typically, the foreign employee quota application window is open from early September to 30 November each year for the use of foreign employees in the following year. The deadline for the 2023 application is extended to the end of January 2023.
According to Joint Prakas 659, if an enterprise hires foreign employees without the approved quota, it may be subject to a fine of up to KHR 2.52 million (USD 630) by the MLVT or KHR 3.6 million (USD 900) by the court. Please note that fines may be imposed in triple in the event of repeat offenses. Additional sanctions, as imposed by the Labour Law, include terms of imprisonment from six days to one month. To our knowledge to date, terms of imprisonment have yet to be strictly enforced.
Foreign Employee Work Permits for 2023
A foreign national must hold a valid work permit in order to lawfully work in Cambodia.
A work permit for foreign employees is valid for only one year. No matter when the work permit for foreign employees is issued by the MLVT, it expires on 31 December of that year. If an enterprise continues to employ foreign nationals in Cambodia for the following year, the enterprise needs to apply for an extension of their foreign work permits by 31 March of the following year.
While pursuant to Prakas 352, a work permit or an extension thereof can be requested online. Foreign employees may also be called to present themselves in person before the MLVT after submission of their work permit applications subject to the discretion of the MLVT.
In accordance with the issuance of Joint Prakas 659, the MLVT has increased its investigations and is actively applying fines against enterprises that have not complied with the above requirements. Additionally, the abovementioned annual fee of KHR 520,000 (USD 130) may be required to be paid accumulatively for each year of non‐compliance by an enterprise (per foreign employee).
According to Joint Prakas 659, if an enterprise hires foreign employee(s) without a work permit, it may be subject to a fine of up to KHR 2.52 million (USD 630) by the MLVT or KHR 3.6 million (USD 900) by the court.
Recently, the MLVT issued Guideline 3005 to clarify the administrative fines that may be imposed by the MLVT labour inspector for failure to obtain a work permit under the Labour Law and Joint Prakas 659. Guideline 3005 provides that if the labour inspector finds less than five foreign employees working without work permits in an enterprise, the labour inspector may impose administrative fines based on the actual number of foreign employees not holding valid work permits. If there are five or more foreign employees, the labour inspector may impose a maximum administrative fine of KHR 12,620,000 (USD 3,155), being five times of the administrative fine imposed by the MLVT.
Please note that fines may be imposed in triple in the case of subsequent and repeat offenses. Additional sanctions, as imposed by the Labour Law, include terms of imprisonment from six days to one month and, in the case of repeat offences, from one to three months. In addition, pursuant to the Law on Immigration and its implementing regulations, the non-compliant enterprise may be subject to a fine of up to KHR 500,000 (USD 125) as imposed by the Ministry of Interior , and in case of subsequent offense(s), imprisonment of up to three months (noting that the foreign employee may be subject to deportation in accordance with the Law on Immigration).
National Social Security Fund (“NSSF”)
An enterprise employing one or more employees is required to register itself and all of its employees with the NSSF within 30 days after the date of its opening. Once registered, the enterprise must pay a monthly contribution to:
- occupational risk insurance (work‐related accidents and occupational diseases);
- health care insurance; and
- pension scheme.
(The pension scheme has been implemented from July 2022, although the contribution payment has effectively commenced from October 2022.)
Each registered enterprise must pay the contribution by the 15th each month and report to the NSSF on the number of employees before the 20th of each month. These dates may be changed subject to periodic notifications issued by the NSSF. The monthly contribution for the pension scheme must be made together with contributions for the occupational risk and health care schemes.
Seniority Pay for Employees under Unspecified Duration Contract (“UDC”)
Seniority pay equal to 15 days of wages and fringe benefits per year must be paid to employees who are employed under UDCs during on-going employment every six months per year, divided into 7.5 days of wages and other benefits to be paid in June and 7.5 days of wages and other benefits to be paid in December.
Large Employer Obligations
When an enterprise employs 100 or more employees, the company must employ 1% of its total workforce as qualified disabled persons and report to the MLVT and the Ministry of Social Affairs, Veteran and Youth Rehabilitation in January each year.
An enterprise employing more than 60 employees is required to conduct annual training of apprentices based on the following quota in proportion to the enterprise’s total workforce:
- 10% for enterprise that employs between 61 to 200 employees;
- 8% for enterprise that employs between 201 to 500 employees; and
- an additional 4% for every further 500 employees at the enterprise that employs more than 51 employees, provided that a maximum of 110 apprentices may be trained by an enterprise in one year.
The deadline for fufiling the training of apprentices is 31 October each year.
It is important to note that the enterprises that have not fulfilled the obligations regarding the training of apprentice must submit a request to the MLVT for payment of tax in lieu of training the apprentices, in an amount equivalent to 1% of total annual salary of all employees per year.
DFDL Services
DFDL Cambodia provides a full range of services to assist clients in meeting their compliance obligations as set out above. These include:
- Assistance with the preparation of annual Tax on Income returns,
- Assistance with the preparation of local Transfer Pricing files,
- Assistance with the application for Patent Tax Certificates, Certificates of Compliance and Annual Declaration of Commercial Enterprise,
- The provision of corporate secretarial services,
- Assistance with labor compliance requirements
For any further information regarding this update please get in touch with our key contacts below or your usual DFDL advisor.
Tax services required to be undertaken by a licensed tax agent in Cambodia are provided by Mekong Tax Services Co., Ltd, a member of DFDL and licensed as a Cambodian tax agent under license number – TA201701018.
The information provided here is for information purposes only and is not intended to constitute legal advice. Legal advice should be obtained from qualified legal counsel for all specific situations.